Quality Definition
The definition of quality is different in a different area or changes as per the nature of the product.
Quality is defined as the degree of excellence which a thing possesses.
OR
It is a relative measure of product goodness and quality standards may fluctuate depending on customer requirements and on product availability.
OR
In other words, the Quality of the product is related to features of the product of its usefulness. Consequently, it depends on the characteristics of the product.
OR
On the other hand, In some sectors of business like schools, banks, transport, insurance, etc, it is called the quality of service. So, it depends on how excellent one serves the public.
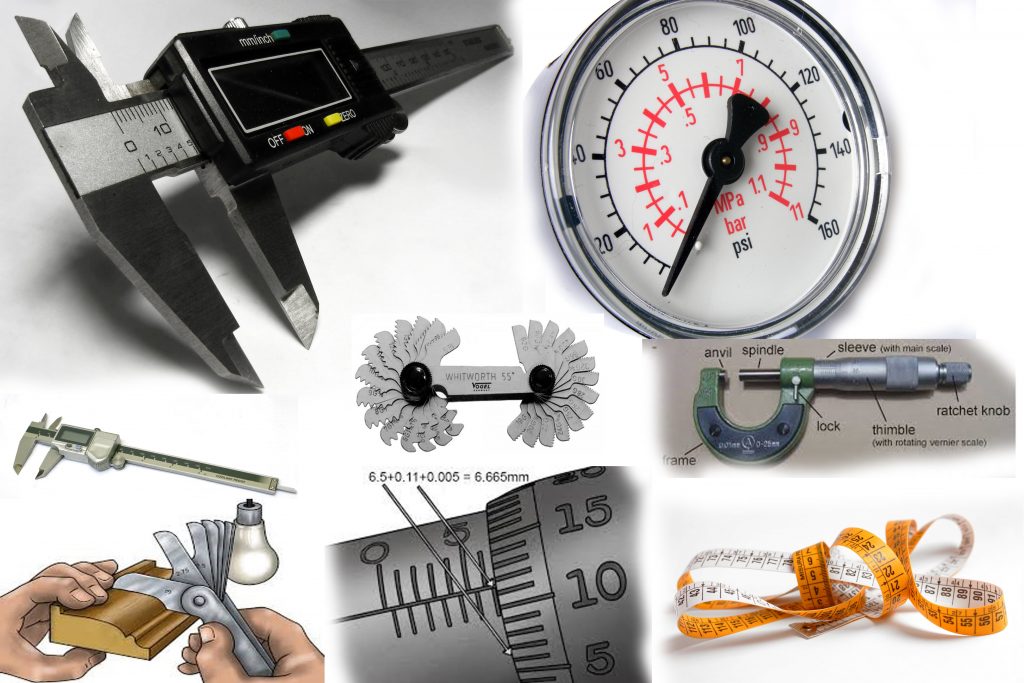
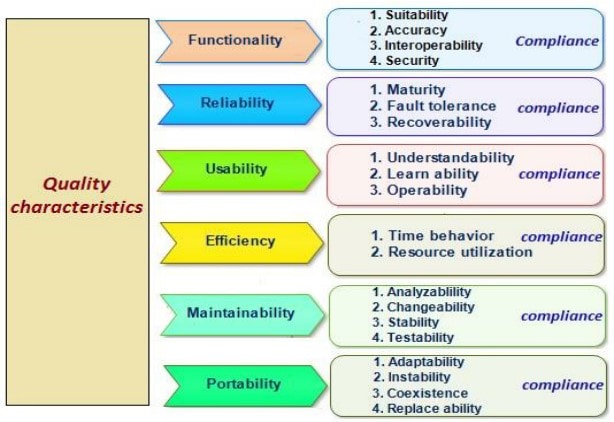
Quality Characteristics:-
Quality Control (QC)
It means observing and measuring actual performance, comparing with standards, and taking control action if required.
In addition, QC is nothing but a procedure intended to ensure that a manufactured product adheres to meets the requirements of the client or customer.
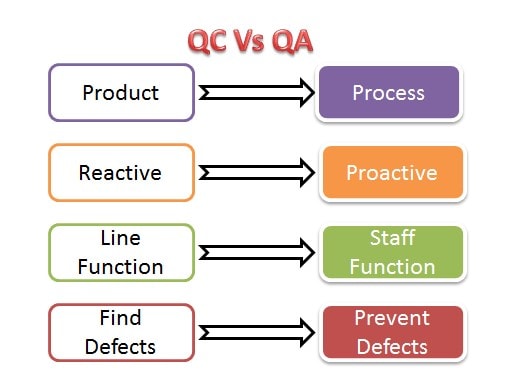
QC (Quality Control) is similar to QA (Quality Assurance), but not identical to QA.
Loop steps of QC
- Set a quality standard.
- Plan for achieving the required quality.
- Inspection and checking plan.
- Measure actual performance.
- Get the difference between measured and standards.
- Take necessary action if required.
Quality of Design
It is concerned with the tightness of the specifications for the manufacturing of the product.
Therefore, we should consider performance, overload capacity, efficiency, all types of failures like stress, wear, shocks, vibration, etc.
Quality of Conformance
It is concerned with how well the manufactured product conforms to the quality of design.
Quality of Performance
It is linked with how well the produced product gives its performance related to stated accept.
The quality of performance certainly influenced by two factors:- Quality of design & Quality of conformance.
Therefore, As a result
Quality of Performance = (Quality of Design) + (Quality of Conformance).
Reliability
Reliability can be the ability of a product to perform a required function under stated conditions for a stated period of time without failure.
Therefore goals of reliability can be finalized by using a three-phase procedure:-
- Budgeting
- Predication
- Analysis.
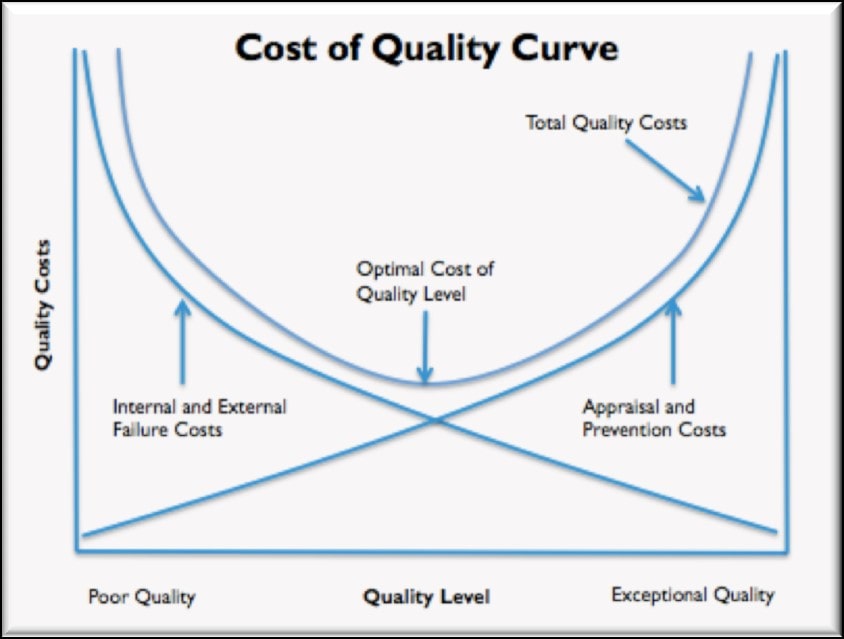
Cost Of Quality
The cost of carrying out the company’s quality function i.e. meeting the quality needs of the customers is known as the Cost of Quality.
However, these include:-
1) Market research cost.
2) The Product R&D (Research & Development) costs.
3) Inspection and test costing.
4) Cost of scrap & Quality failures.
5) QA cost.
6) Cost of field service.
7) Design Cost.
However, as per ASQC (American Society for Quality Control), the quality costs can be divided into three categories:
- Cost of prevention.
- The cost of an appraisal.
- And the cost of failure (internal & external).
1.Cost of prevention
Firstly, prevention costs are incurring to prevent or avoid quality problems.
Meanwhile, these costs are related to the design, implementation, and maintenance of the quality management system.
They are incurring before the actual operation, and in addition, they could include:
| Product or service requirements | Establishment of specifications for incoming materials, processes, finished products, and services |
| Quality planning | The creation of plans for quality, reliability, operations, production, and inspection |
| QA | Creation, and maintenance of the quality system |
| Training | Development, preparation, and maintenance of programs. |
2.Cost of appraisal
Firstly, Appraisal costs are related to measuring and monitoring activities related to quality.
Therefore these costs are related to the suppliers’ and customers’ evaluation of purchased materials, processes, products, and services to ensure that they conform to specifications.
In addition, they could include:
| Verification | Checking of incoming material, process setup, and products against agreed specifications |
| Quality audits | Confirmation that the quality system is functioning correctly |
| Supplier rating | Assessment and approval of suppliers of products and services |
3.Cost of failure (internal & external)
a) Internal failure costs:-
Internal failure costs include remedy defects discovered before the product or service is delivered to the customer.
In conclusion, these costs occur when the results of work fail to reach design quality standards and are detected before they are transferred to the customer.
Moreover, they could include:-
| Waste | Performance of unnecessary work or holding of stock as a result of errors, poor organization, or communication. |
| Scrap | Defective product or material that cannot be repaired, used or sold |
| Rework or rectification | Correction of defective material or errors |
| Failure analysis | The activity required to establish the causes of internal product or service failure |
b) External failure costs:-
External failure costs are incurred to remedy defects discovered by customers.
In these costs generate when products/services, that fail to reach design quality standards are not detected until after transfer to the customer.
In addition, they could include:-
| Repairing & servicing | Returned products from customers and products which are in the field. |
| Warranty claims | Failed products that are replaced or services and that are re-performed under a guarantee |
| Complaints | All work and costs associated with handling and servicing customer’s complaints |
| Returns | Handling and investigation of rejected or recalled products, including transport cost |
Cost of quality and organizational objectives
The cost of quality is nothing but, the costs of doing a quality job, conducting quality improvements, and achieving goals must be carefully managed. So that the long-term effect of quality on the organization is a desirable one.
Meanwhile, these costs must be a true measure of the quality effort, and they are best determined from an analysis of the costs of quality.
In short, such an analysis provides a method of assessing the effectiveness of the management of quality. It also helps in determining problem areas, opportunities, savings, and action priorities.
It is also an important communication tool. Philip Crosby demonstrated what a powerful tool it could be to raise awareness of the importance of quality. He referred to the measure as the “price of nonconformance” and as a result argued that organizations choose to pay for poor quality.
Many organizations will have true quality-related costs as high as 15 to 20 percent of sales revenue likewise, and some going as high as 40 percent of total operations.
A general rule of thumb is that the costs of poor quality in a thriving company will be about 10 to 15 percent of operations likewise. Effective quality improvement programs can reduce this substantially, thus making a direct contribution to profits.
The quality cost system, once established, should become dynamic and have a positive impact on the achievement of the organization’s mission, goals, and objectives.
Cost of Quality Curve
Value of Quality
It is defined as the, return direct/indirect gained by the manufacturer, because of the mission of QC.
In other words, By using the best quality of the product, one of the companies can get a maximum share in profit and enjoy the market conditions.
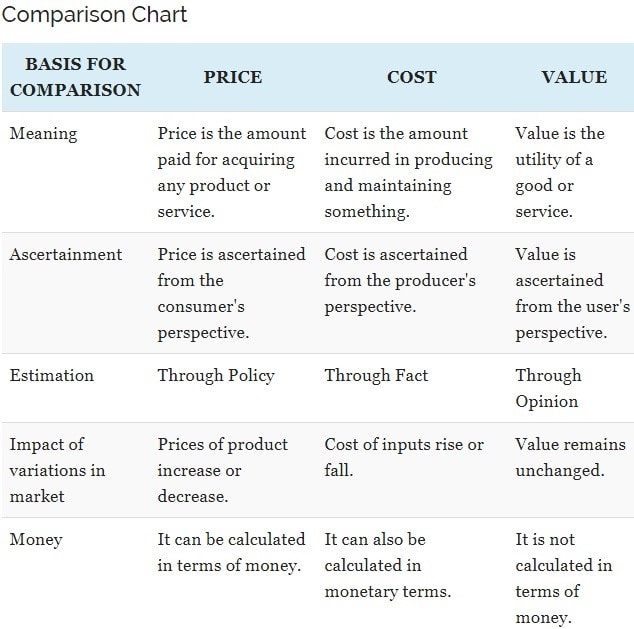
Comparison Chart of Price, Cost & Value
Quality Assurance (QA)
QA is defined as all the planned and systematic activities implemented within the quality system. And that can be demonstrated to provide confidence that a product or service will fulfill requirements for quality.
In conclusion, QA is the way of avoiding mistakes, and defects in manufactured products, so that we minimize problems when delivering products or services to the customer.
Stages of QA:-
1.Design stage (Related to Quality of Design).
2.Manufacturing stage (Related to Quality of manufacturing conforming).
3.Field stage (Related to Quality of Performance).
As a result,
QA = (Quality of design) + (Quality of conformance) + (Quality of performance) .
Inspection
Inspection is nothing but checking of material, components of products at various stages in manufacturing.
In addition, inspection involves checking something. We may inspect a building to make sure as a result is that it meets specific standards.
Types of Inspection:-
1)Offline inspection.
2)On line inspection.
Difference Between Inspection & QC

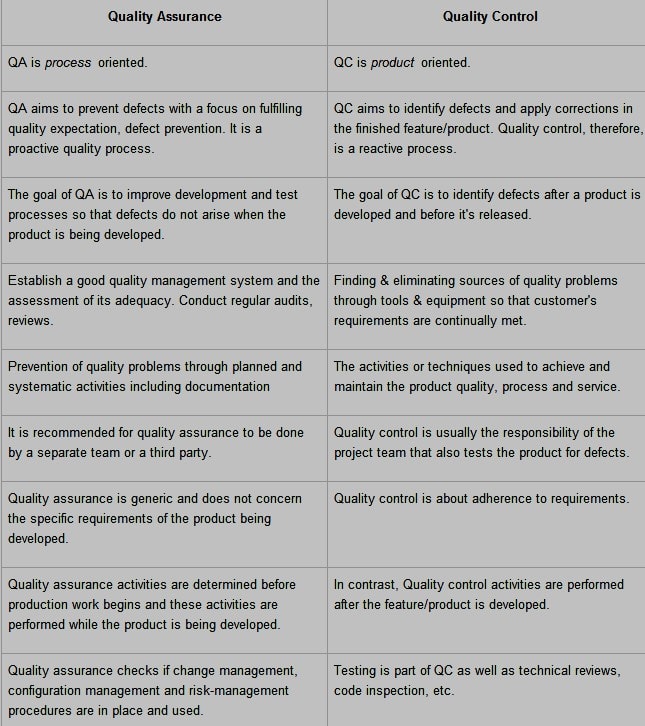
Difference Between QC & QA
In addition, make sure you also check our other amazing article on Metrology.
Meanwhile, this article has all information regarding metrology, metrological instruments, basics about least count, and many more.
Android (3) apps (6) Baby Products (10) best (1) Free (1) Health (20) Health Related Products (10) Measurement (2) Mechanical Engg (2) Metrology & Quality Control (2) Products (12) Rainy Season (1) udyojak (10) अभ्यास संबंधित (4) अमिताभ बच्चन (1) उद्योग (13) उपाय (17) कोल्हापूर (1) ग्रामीण (18) ट्रक (4) देश (20) पैसे (6) प्रेरणा (3) फडणवीस (4) फायदा (3) बिजनेस (18) मशीन (18) महाराष्ट्र (21) महाराष्ट्राचे राजकारण (7) मोदी (2) मोबाइल (3) योजना (1) रजिस्टर (6) रेकॉर्ड (2) लहान बाळ (7) वायरल (4) विदेश (4) विद्यापीठ (3) व्यवसाय (18) शरद पवार (2) शेती (5) सण (19) स्पीकर (1) स्वयंपाक (7) हिंदू (19)





